In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about where to plant blueberry bushes for optimum growth and production.
Understanding Blueberry Requirements
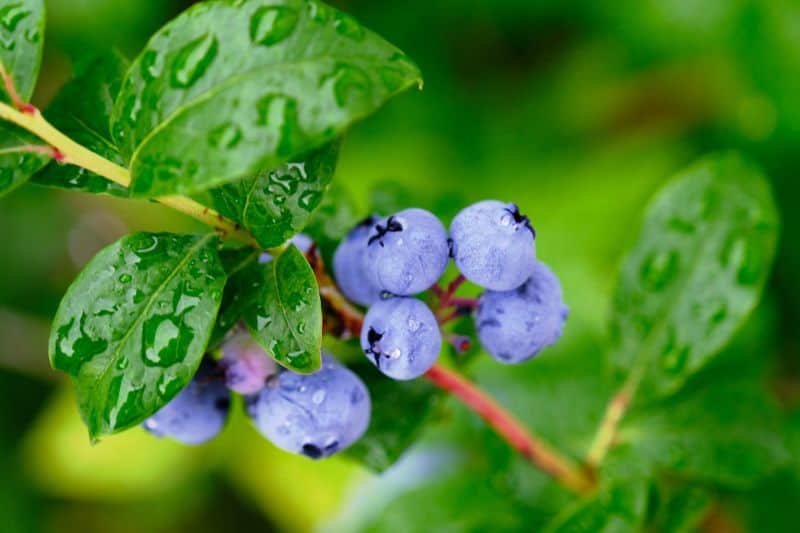

Before diving into the specifics of plant placement, it’s crucial to understand what blueberries need to thrive. Blueberry bushes are particular about their growing conditions, and understanding this will help you choose the most suitable location.
Soil Composition
Acidity Matters: Blueberries prefer acidic soils with a pH between 4.5 and 5.5. This acidity is essential for the plants to absorb the necessary nutrients.
Drainage: Well-draining soil is crucial. Blueberries are susceptible to root rot if they sit in waterlogged soil. Sandy loam is ideal, but if your soil is heavy clay, consider amending it or creating raised beds.
Sunlight Needs
Blueberries are sun-loving plants that thrive in full sunlight. Ideally, they should receive at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. Insufficient light can lead to poor fruit production and weak plant growth.
Water Requirements
While blueberries need ample water to establish their roots, they do not tolerate drought or oversaturation. Consistent, moderate watering is critical, especially during the establishment phase. A location with easy access to irrigation or a natural water source will be beneficial.
Wind Protection
Blueberry bushes can be vulnerable to strong winds, which may damage branches and cause stress to the plants. Planting them near natural windbreaks, such as trees or fences, can offer protection and encourage healthy growth.
Choosing the Right Location

When selecting the perfect spot for your blueberry bushes, consider the following factors that can significantly influence their growth.
Sunny Spots
Maximize Exposure: Look for areas in your yard that have maximum sun exposure, such as south or southwest-facing slopes. Avoid shady areas, as they will stunt the plants’ growth and reduce fruit yield.
Evaluate Existing Trees and Buildings: Before planting, assess how shadows from trees, buildings, or structures move throughout the day. Avoid spots that will be shaded during peak sunlight hours.
Soil Testing
Conduct a Soil Test: Knowing your soil’s pH is critical. Many garden centers provide pH testing kits, or you can send samples to a local extension service. Adjust the pH if necessary, using sulfur to lower it or lime to raise it.
Amendments for Improvement: If your soil is not naturally acidic, consider planting in raised beds filled with an appropriate acidic soil mix or incorporating organic mulch like pine needles or sawdust to gradually acidify your soil.
Proximity to Water Sources
Accessibility is Key: Ensure that your blueberry bushes are planted within a reasonable distance from a water source. A hose or irrigation system will make regular watering easier.
Check Natural Drainage: Avoid low-lying areas where water tends to pool. Instead, choose a slight rise or a slope that helps with both drainage and ensures your blueberry plants will be watered without saturating their roots.
Wind Protection Options
Natural Barriers: Consider planting blueberry bushes near existing trees or shrubs that can serve as windbreaks. Alternatively, erect fencing that doesn’t obstruct sunlight but offers protection from strong winds.
Strategic Layout: When establishing a row of blueberries, orient the rows north to south to minimize wind exposure and ensure that all plants receive sunlight evenly.
Spacing and Layout Considerations
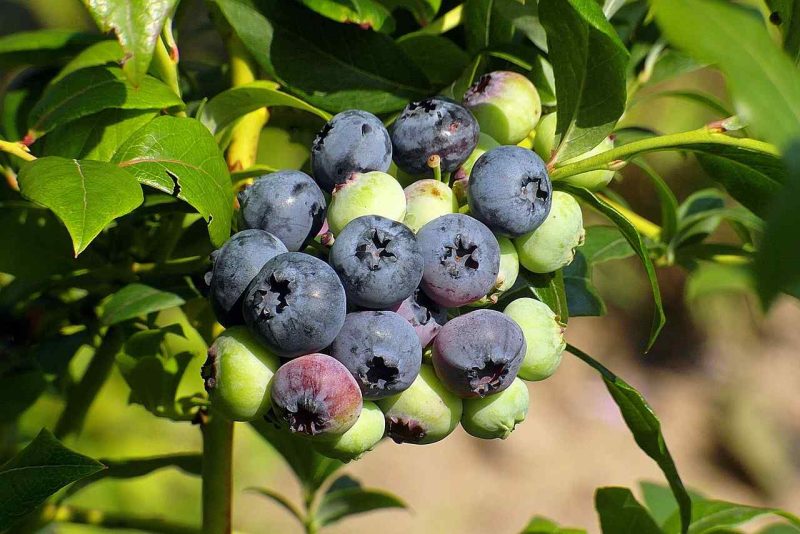

Once you’ve selected your location, understanding how to space your blueberry bushes is essential for their growth and productivity.
Spacing Between Plants
Optimal Planting Distance: Most blueberry varieties need about 4 to 6 feet of space between each bush to allow for airflow and sunlight penetration. This spacing prevents overcrowding and reduces the risk of fungal diseases.
Row Spacing: When planting multiple rows, allow 8 to 10 feet of space between rows. This not only facilitates easy harvesting but also provides adequate air circulation.
Companion Planting
Enhancing Growth: Certain plants can benefit blueberries through companion planting. Herbs like basil or marigold can deter pests, while clover can improve soil nitrogen levels.
Avoiding Companions to Skip: Steer clear of planting blueberries near plants that prefer alkaline soil like asparagus and brassicas, as they can negatively affect each other’s growth.
Design Ideas
Diverse Landscape Integration: Blueberries can be a beautiful part of your landscape design. Consider planting them along borders, as hedging, or even within garden beds to create a natural and visual appeal.
Edible Landscapes: Incorporate blueberries into edible landscapes where they can complement other fruiting plants such as strawberries or raspberries, allowing for a diverse and productive garden space.
Regional Considerations
Understanding your region’s climate is critical when determining how and where to plant blueberries. Different growing zones may have unique challenges and advantages.
Cool Climates
Cold-tolerant Varieties: If you live in a cooler climate, opt for northern highbush or rabbiteye blueberry varieties that can tolerate frost and cold winters.
Mulching Benefits: Use mulch to insulate the roots and regulate soil temperature. Organic materials like wood chips can maintain moisture and improve soil acidity over time.
Warm Climates
Heat-resistant Varieties: In hotter regions, consider southern highbush blueberries that are bred for warmer temperatures. They are more heat-resistant and require less chilling hours for fruiting.
Shade for Protection: Providing some shade during the hottest part of the day can help prevent heat stress. Use shade cloth or strategically place plants that can offer partial shade without blocking vital sunlight.
Humid Regions
Fungal Disease Awareness: High humidity can promote fungal diseases. Consider planting blueberries where there is good air circulation and avoid tight planting arrangements to minimize humidity buildup.
Water Management: Ensuring your blueberry plants are not waterlogged is vital in humid areas. Raised beds or well-drained soil will help mitigate excess moisture and root rot.
Maintenance and Follow-Up Care
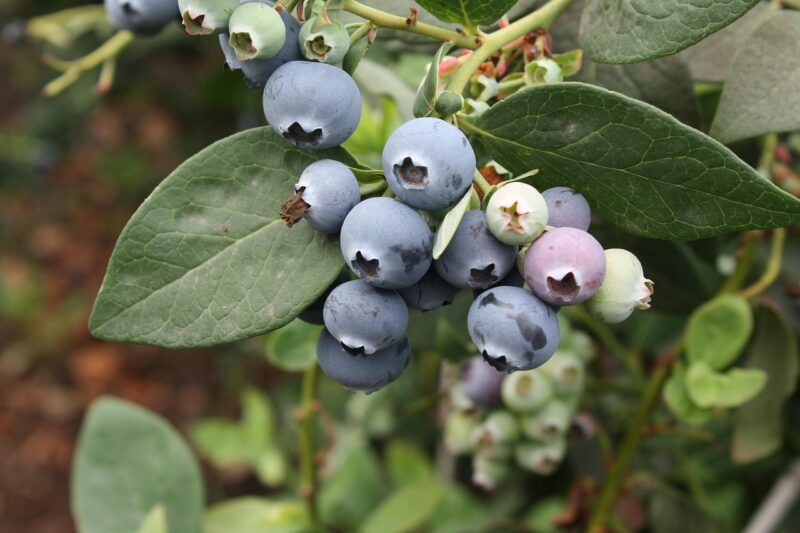

Planting your blueberry bushes correctly is only the beginning. Proper maintenance is critical for their health and productivity.
Fertilization Practices
Nutrient Needs: Blueberries require specific nutrients for optimal growth. Use fertilizers specifically designed for acid-loving plants, and apply them sparingly in spring.
Timing of Application: Early spring is the best time for fertilization, just before the plants begin to bloom. This ensures they have the nutrients they need during the flowering and fruiting stages.
Pruning for Productivity
Timing Matters: Pruning during late winter or early spring promotes healthy growth. Remove any dead or crossing branches to encourage better air circulation and sun exposure.
Train the Bushes: Early on, train the bushes by selecting a few strong stems to focus on, allowing the plant to develop a sturdy structure for future fruit production.
Pest and Disease Management
Regular Monitoring: Check your plants frequently for signs of pests such as scale or aphids. Early detection can help manage problems before they escalate.
Organic Solutions: Consider natural deterrents like neem oil or insecticidal soap to address pest issues without harming beneficial insects.
Fungal Disease Prevention: Utilize proper spacing and watering techniques to avoid fungal diseases, and select resistant varieties if you are in areas prone to such issues.
Harvesting Blueberries

After patiently nurturing your bushes, the time will come to harvest your delicious blueberries. Understanding when and how to harvest ensures you enjoy the fruits of your labor.
Ideal Harvest Time
Timing: Blueberries typically ripen during late summer to early fall, depending on the variety and climate. Monitor your bushes closely as berries change from green to a deep blue color.
Taste Check: For the best flavor, harvest berries that are fully ripe. They should easily come off the stem when gently rolled between your fingers.
Best Practices for Harvesting
Gentle Handling: Blueberries are delicate. Use care during harvesting to avoid bruising the fruit and damaging the plant.
Harvest Regularly: Picking berries regularly, about every few days, can improve the overall yield of the bushes by encouraging additional fruit set.
Conclusion
Planting blueberries can be a fulfilling project that pays off with delicious, healthy fruit for years to come. Understanding where to plant blueberry bushes involves considering soil, sunlight, water access, and regional climate specifics. By carefully choosing the right location, spacing, companion plants, and maintaining their health, you can create a thriving blueberry patch in your garden.





