Are roses perennials? In this in-depth guide, we will uncover the intricacies of how roses are classified, their growth habits, care requirements, and much more. So, grab a cup of tea, and let’s delve into the enchanting world of roses!
Are Roses Perennials? The Floral Classification

Roses belong to the genus Rosa, which is part of the larger Rosaceae family. Most rose varieties are considered perennial shrubs or climbing plants. This classification means that roses, in their typical forms, grow back each season, exhibiting a cycle of blooming, dormancy, and regrowth.
However, it’s worth noting that not all roses are equal. Climbing roses, shrub roses, and hybrid tea roses may exhibit different growing patterns and care needs. Understanding these varieties will help clarify how different types of roses behave throughout the seasons.
The Different Types of Roses
Hybrid Tea Roses: These are perhaps the most popular type of roses, characterized by their long stems and classic, large blooms. They are treated as perennials in most climates but may require special attention in colder regions, as their woody stems can be susceptible to winter damage.
Floribunda Roses: Known for their clusters of blooms, floribundas also behave as perennials. They tend to be hardier and can withstand varied climates better than some hybrid varieties.
Climbing Roses: These roses can transform an ordinary space into a floral paradise by climbing trellises or walls. As perennials, they provide stunning displays year after year, but they may need pruning to encourage healthy growth.
Shrub Roses: Often tougher and more resilient than other types, shrub roses are ideal for low-maintenance gardens. They thrive as perennials, requiring less care while offering continuous blooms.
Miniature Roses: Although small in stature, miniature roses are perennial and can be grown in containers, making them a favorite for patios and small spaces.
With this broad spectrum of rose types, it’s clear that roses, in general, can be classified as perennials. However, the specific growing conditions and care practices will significantly affect their longevity and health.
The Lifespan of Roses

While most rose varieties are perennials, it’s crucial to understand their average lifespan and the factors that influence it. Under optimal conditions, many roses can thrive for several decades, but this can vary depending on the rose type and care provided. Here are some key factors that affect the lifespan of roses:
Climate
Roses adapt well to a range of climates, but extreme conditions—whether too hot or too cold—can stress the plant and shorten its lifespan. Hardy varieties tend to thrive in cooler areas, whereas tender types may struggle in regions that experience harsh winters.
Soil Quality
The fertility and drainage capability of the soil play a significant role in a rose’s health. Well-draining, nutrient-rich soil fosters longevity. Conversely, poor soil conditions may lead to diseases and shorter lifespans.
Watering Practices
Roses need consistent moisture, but overwatering or allowing their roots to sit in water can lead to root rot, drastically affecting their life span. Striking the right balance is crucial.
Pest and Disease Management
Pests such as aphids or diseases like black spot can severely hinder a rose’s vitality. Effective management through organic or chemical treatments can help secure a rose’s perennial status.
Pruning and Care
Regular maintenance, including pruning dead or diseased wood, can promote healthy growth and flowering. Neglecting this care can lead to a shorter lifespan.
Understanding these factors gives gardeners insight into how best to care for their roses and ensure they flourish as perennials in their gardens.
Roses in Different Growing Zones
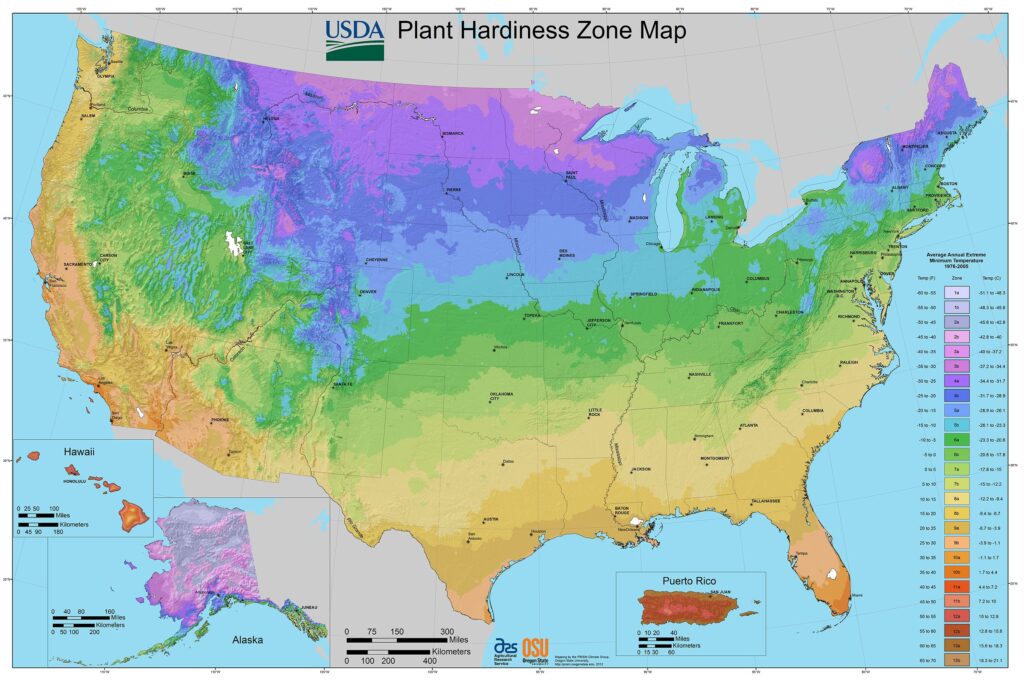
While many roses are classified as perennials, their ability to thrive can depend largely on the hardiness zone where they are planted. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) hardiness zone map is a key reference for gardeners in determining which rose varieties will grow best in their climate.
Hardiness Zones Explained
The USDA hardiness zones range from 1 to 13, with Zone 1 being the coldest and Zone 13 being the warmest. Most roses are suited to hardiness zones 3 through 10. Here’s how different rose varieties generally fare:
Zone 3 to 4: These regions require cold-hardy roses, such as ‘Knock Out’ rose and many old-fashioned varieties. These roses are excellent perennials in colder climates.
Zone 5 to 6: Roses suited for these zones include hybrid teas and floribundas. With proper care, they can thrive throughout the growing season.
Zone 7 to 10: Tender roses flourish here, including many climbing and no-fragrance roses. However, even within these zones, attention to winter protection can enhance perennial growth.
Understanding these zones allows gardeners to select the best rose varieties for their specific conditions, ultimately ensuring a successful perennial garden.
Growing and Caring for Roses

To truly appreciate roses as perennials, one must understand how to grow and care for them. While they can be resilient, they do require specific attention to thrive season after season.
Soil Preparation
As mentioned earlier, the soil is critical for rose health. It must be well-draining to prevent waterlogging and associated diseases. Improve the soil’s fertility by adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure. Roses flourish in slightly acidic to neutral pH levels (around 6.0 to 6.8).
Planting Tips
When planting roses, ensure they are in a location that receives full sun for at least six hours a day. When you dig the hole for your rose, make it twice as wide as the root ball but no deeper than the root ball itself. Proper spacing is vital to allow for air circulation, which helps to prevent disease.
Watering Techniques
Water roses deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between watering. Consistent moisture is essential, especially in the active growing season. Consider using soaker hoses or drip irrigation to keep water off the foliage, reducing the risk of diseases.
Fertilization Regimen
Feeding roses a balanced fertilizer can encourage abundant blooms. Look for a fertilizer formulated specifically for roses and follow the application advice on the package. Typically, a spring feeding and subsequent summer feeding work well.
Pruning Practices
Pruning is a crucial aspect of rose care, promoting air circulation and removing dead or diseased wood. The best time to prune is in late winter or early spring, just before new growth appears. Aim to shape the plant, removing any growth that crosses or is too crowded, and cut back to an outward-facing bud.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitoring for pests like aphids, spider mites, and diseases such as powdery mildew is essential. Integrated pest management (IPM) strategies using companion planting, beneficial insects, and organic solutions can help mitigate the impact of pests and diseases, ensuring healthy, perennial roses.
The Symbolism of Roses in Culture

Beyond their biological classification and horticultural requirements, roses hold a significant place in culture and symbolism. This connection enhances our appreciation of them as perennials—symbols of enduring beauty and resilience.
Roses in Literature and Art
Throughout history, roses have been woven into the fabric of literature and art. From Shakespeare’s romantic verses to modern poetry, the rose is often used to symbolize love, beauty, and even sacrifice. Their vivid colors have inspired countless paintings, embodying emotions that span from joy to sorrow.
The Language of Roses
Known as the “language of flowers” or floriography, roses enter into conversations filled with meaning. Different colors and varieties of roses convey distinct emotions: red roses represent passionate love, white roses signify purity and innocence, while yellow roses symbolize friendship and joy. This symbolism adds a layers to their existence, emphasizing their perennial relevance in human experiences.
Cultural Significance
Roses are ubiquitous in cultural celebrations—from weddings and anniversaries to funerals and memorials. Their versatility makes them a universal gift, representing love, respect, and remembrance through generations. The timelessness of roses reflects the sentimentality behind giving, making them beloved worldwide.
The Future of Roses: Hybridization and Genetic Research

The world of roses is continually evolving with research into hybridization and genetic variations. These developments are essential to enhancing their hardiness and beauty, adding further dimensions to our understanding of them as perennials.
Hybridization Efforts
Gardeners and horticulturists have long engaged in hybridization to create robust rose varieties resistant to diseases and adverse conditions. This practice ensures that roses can adapt to changing climates while enhancing their aesthetic appeal.
Genetic Research
Cutting-edge research projects now delve into the genetic makeup of roses, aiming to understand and manipulate traits that promote resilience. Insights gleaned from genetic studies pave the way for breeding new varieties that will thrive despite emerging challenges such as climate change and pests.
Sustainability and Conservation
As gardeners and consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainable practices in rose gardening are gaining traction. Choicely selecting varieties that require fewer inputs and managing roses in ways that promote biodiversity highlights an economic approach to perennial gardening.
Conclusion: Celebrating Roses as Perennial Beauties
In summarizing the characteristics of roses in relation to perennials, it is evident that these magnificent plants not only thrive season after season but also hold deep emotional resonance in our lives. By appreciating their classification, care requirements, cultural significance, and ongoing developments in horticulture, we can better embrace the beauty of roses as perennials.





