Best Salvia Varieties
| Image | Name | Rating | Shop |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Salvia Sclarea Clary Sage |  | |
 | Salvia Coccinea Sage Scarlet Wild Flowers |  | |
 | Salvia Farinacea Blue Victory Flower Seeds |  | |
 | Blue Queen Salvia Seeds |  |
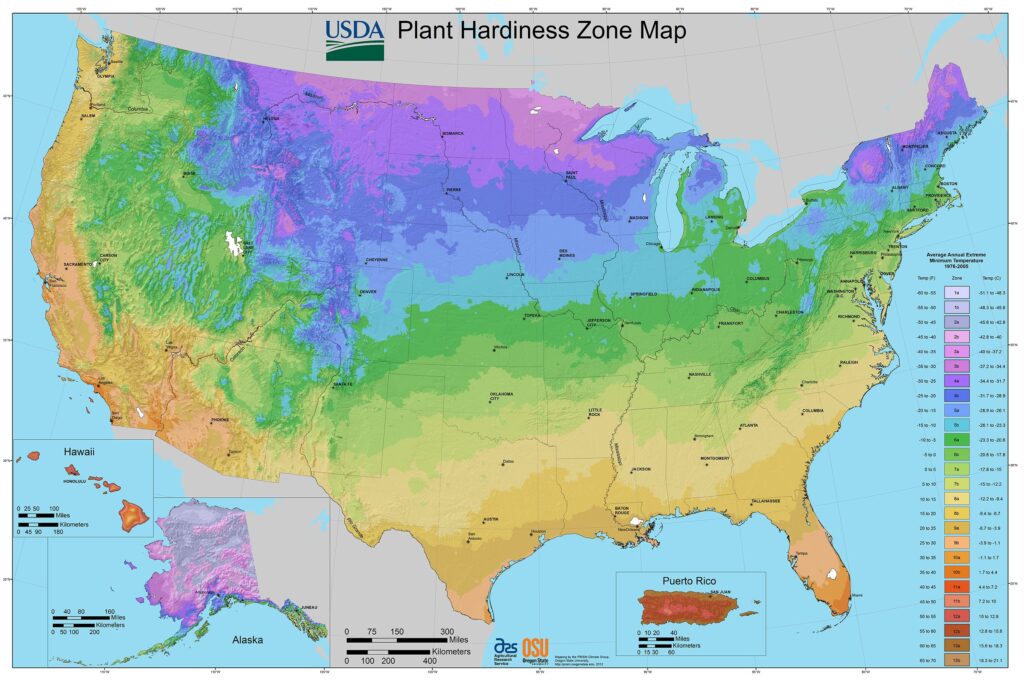
Salvia Hardiness Zones
Salvia, with its wide variety of species and cultivars, boasts impressive adaptability across different climates. Depending on the specific type, Salvia can thrive in a range of hardiness zones, typically spanning from zones 4 to 11 on the USDA hardiness scale. Before selecting your Salvia plants, check the hardiness zone recommendations to ensure they are suitable for your region’s climate.
How Much Sun Does Salvia Need
Salvia plants are sun-loving perennials that thrive in full sunlight. For optimal growth and flowering, it is recommended to plant Salvia in locations where they can receive at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day. In areas with extremely hot summers, some afternoon shade can help protect Salvia plants from intense heat. However, insufficient sunlight may result in leggy growth and fewer blooms, so prioritize planting Salvia in sunny spots within your garden.
Salvia Soil Requirements
When it comes to soil, Salvia prefers well-drained, moderately fertile soil that retains some moisture without becoming waterlogged. Whether you’re planting Salvia in garden beds, containers, or borders, ensure the soil is loose, airy, and rich in organic matter. Sandy loam or loamy soil types are ideal for Salvia cultivation, providing the perfect balance of drainage and moisture retention necessary for healthy root development.
Salvia Soil pH
The optimal soil pH for Salvia cultivation ranges from slightly acidic to neutral, typically between 6.0 and 7.0. Conduct a soil pH test before planting Salvia to determine if any adjustments are necessary. If the soil pH is outside the recommended range, amend it accordingly with organic matter or pH-adjusting additives to create suitable growing conditions for your Salvia plants.
Salvia Plant Spacing
When planting Salvia, provide adequate spacing between individual plants to allow for proper air circulation and prevent overcrowding. Depending on the specific variety and growth habit, Salvia plants typically require spacing of 12 to 24 inches apart. This spacing allows each plant ample room to spread out and flourish, promoting healthier growth and more abundant blooming throughout the growing season.
Salvia Water Requirements
While Salvia plants are relatively drought-tolerant once established, they still require regular watering, especially during periods of prolonged drought or extreme heat. Water newly planted Salvia regularly to help establish strong root systems. Once established, water Salvia plants deeply and infrequently, allowing the top inch of soil to dry out between waterings. Avoid overwatering, as excessively wet soil can lead to root rot and other moisture-related issues.
Salvia Temperature Requirements
Salvia plants thrive in warm temperatures and are well-suited to regions with mild to hot summers. Most Salvia varieties can tolerate temperatures ranging from 60°F to 90°F, making them ideal choices for gardens in temperate and subtropical climates. However, some species may exhibit sensitivity to frost or freezing temperatures, so it’s essential to select Salvia cultivars that are suitable for your specific climate zone.
Salvia Humidity Requirements
Salvia plants are adaptable to a wide range of humidity levels, from dry arid climates to humid regions. While they can tolerate moderate humidity, excessive moisture in the air may increase the risk of fungal diseases such as powdery mildew. To minimize humidity-related issues, provide adequate spacing between Salvia plants to promote airflow and avoid overhead watering, which can contribute to leaf moisture buildup.
Salvia Fertilizer Requirements
Salvia plants are relatively low-maintenance and do not require heavy fertilization to thrive. In most cases, a light application of balanced fertilizer in spring or early summer is sufficient to support healthy growth and flowering. Use a slow-release fertilizer or organic compost to provide essential nutrients to the soil without risking overfeeding. Avoid excessive nitrogen fertilizers, as they may encourage lush foliage growth at the expense of flower production.
Salvia Pests
Salvia plants are generally resistant to pests, but they may occasionally attract common garden pests such as aphids, spider mites, or whiteflies. Keep an eye out for signs of pest infestation, such as distorted leaves or sticky residue on foliage. If pest problems arise, treat affected plants promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil to control the infestation and prevent further damage.
Salvia Diseases
While Salvia plants are relatively disease-resistant, they may be susceptible to fungal diseases such as powdery mildew or root rot, especially in humid or poorly ventilated conditions. To minimize the risk of disease, avoid overhead watering, which can lead to leaf moisture buildup and fungal growth. Provide adequate spacing between plants to improve airflow and remove any diseased or damaged foliage promptly to prevent the spread of infection. Additionally, ensure proper soil drainage to prevent waterlogged conditions that can promote root rot. By following these care guidelines, you can enjoy healthy, vibrant Salvia plants in your garden year after year.