This guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of when to plant sweet potatoes, taking into account the climate, soil preparation, and other crucial factors that contribute to a successful harvest.
Understanding Sweet Potatoes and Their Growing Seasons

Before delving into specifics about planting times, it’s important to understand the nature of sweet potatoes. The sweet potato belongs to the Convolvulaceae family and thrives in warm climates. Unlike regular potatoes, which are grown from seed potatoes, sweet potatoes are cultivated from slips—young shoots that sprout from mature tubers.
Sweet potatoes require a long growing season, typically ranging from 90 to 120 days, depending on the variety. This means planting should occur after the last frost date in your area to ensure that your plants get the warmth they need to flourish.
The Ideal Climate for Sweet Potatoes

Climate is the cornerstone of successful sweet potato cultivation. Understanding your local growing conditions is essential when determining the appropriate planting time.
Temperature
Sweet potatoes flourish in warm conditions, with ideal soil temperatures ranging from 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C). If the soil temperature is lower than 60°F (15°C), the plants will struggle to grow, and you may risk stunted growth or rot. To monitor soil temperature, you can use a soil thermometer, which can be a handy tool for any gardener.
Frost Dates
Frost is the enemy of sweet potatoes. They are particularly sensitive to cold weather, which can kill the young plants quickly. Knowing your area’s last frost date is crucial since you should plant your sweet potatoes about two to four weeks after this date. To effectively find this date, you can consult local agricultural extensions or online gardening resources that provide frost date information based on your zip code.
Planning Your Planting Date
With a solid understanding of climate considerations, the next step is to plan your planting date strategically.
Checking the Weather Patterns
As climate change continues to affect weather patterns, it’s wise to keep an eye on local conditions leading up to your planting time. If a late frost is forecasted, it might be wise to delay planting and protect your slips with row covers or cloches if you’ve already set them out.
Region-Specific Timing
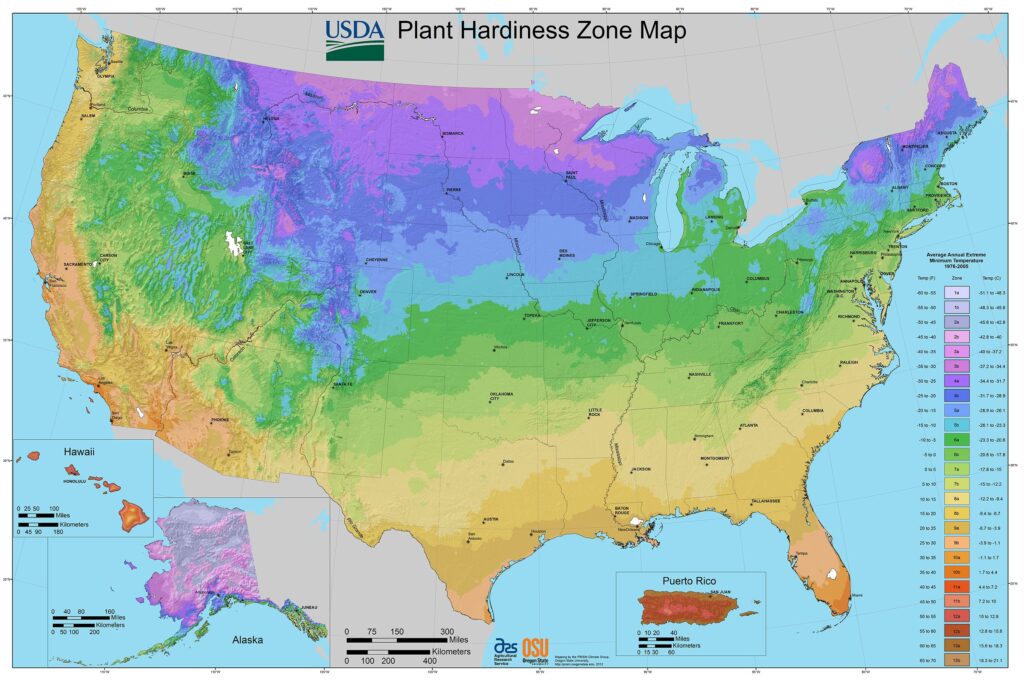
Different regions have distinct growing seasons, so adapting your planting schedule to your local climate is vital. For instance:
Southern US (USDA Zones 8-10): Here, the growing season is longer, and you can typically plant sweet potatoes as early as mid-April.
Midwestern US (USDA Zones 5-7): In these regions, aim for planting between late May and early June to ensure that you avoid frost.
Northern US (USDA Zones 3-5): In cooler areas, the best time to plant is usually in June when the danger of frost has passed.
Preparing Ideal Conditions for Planting
Preparation is key to successful gardening, and sweet potatoes are no exception. Once you’ve determined your planting date, it’s essential to create the right environment for the slips.
Soil Preparation

Sweet potatoes thrive in well-drained, sandy loam soil with a pH between 5.8 and 6.2. Here are some steps to prepare your soil:
Testing Soil: Before planting, test your soil’s pH and nutrient content. You can purchase home test kits or send a sample to a local extension service.
Enriching the Soil: If your soil is lacking nutrients, incorporating compost or well-rotted manure can improve fertility.
Tilling: Break up the soil to a depth of about 12 inches (30 cm) to allow for healthy root development. Sweet potatoes grow best when they have room to expand.
Creating Ridges: Consider planting sweet potatoes on raised ridges to promote drainage and warming soil conditions. Ridges also help to keep the tubers from rotting.
Planting Your Sweet Potatoes

Once you’ve prepared your soil and planned your date, it’s time for the fun part—planting the slips!
Choosing the Right Slips
Select healthy sweet potato slips from local garden centers or reputable suppliers. You might even consider starting slips yourself by submerging sweet potatoes in water, ensuring they receive light and warmth to encourage sprouting.
Planting Depth and Spacing
It’s essential to plant your sweet potato slips correctly. Here’s how:
Depth: Plant the slips so that about two-thirds of the slip is buried in the soil, leaving the top exposed. This positioning allows for proper growth while providing stability.
Spacing: Space the slips about 12 to 18 inches apart to give each plant enough room to thrive. Rows should be spaced at least 3 feet apart to allow for proper air circulation.
Watering and Care After Planting
Post-planting care is crucial for establishing healthy sweet potato plants.
Watering
Sweet potatoes need consistent moisture, especially during their early growth stages. Here’s a watering guideline:
Initial Watering: Thoroughly water the slips immediately after planting to settle the soil around the roots.
Ongoing Watering: Provide weekly watering, especially during dry spells. An inch of water every week is sufficient, but be cautious of overwatering, which can lead to rot.
Mulching
Applying a layer of organic mulch can help retain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain consistent soil temperature. Straw, grass clippings, or shredded leaves work well as mulch.
Monitoring Growth and Signs of Problems
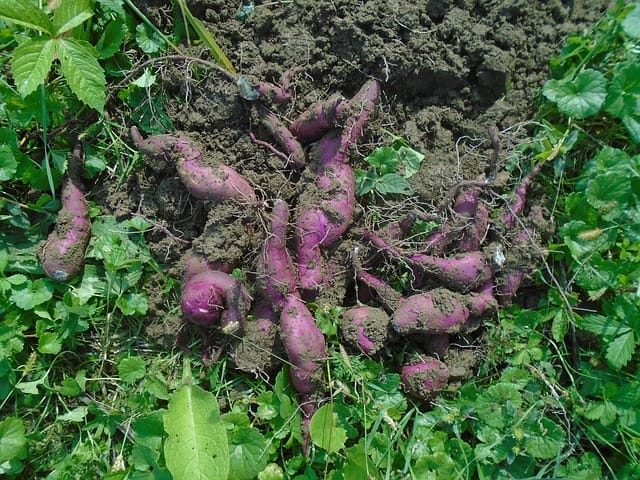

As your sweet potatoes grow, keep an eye out for any issues that might arise.
Pest Management
While sweet potatoes are relatively pest-resistant, they can still be affected by insects like aphids, beetles, and wireworms. Regularly inspect your plants and use organic pesticides if infestations occur.
Disease Awareness
Fungal diseases, such as root rot and leaf blight, can be detrimental to sweet potatoes. Ensure you’re providing well-draining soil and correct watering practices to mitigate these risks.
Signs Your Sweet Potatoes Are Ready to Harvest

After a few months of growth, it’s time to get excited about the harvest! Recognizing when sweet potatoes are ready to dig up is an important part of the growing process.
Timing is Everything
Typically, sweet potatoes are ready to be harvested 90 to 120 days after planting, depending on the variety. Signs that your sweet potatoes are ready include:
Leaves Yellowing: Once the leaves begin to yellow and die back, it’s a good indication that the tubers are mature.
Tops Falling Over: If the vines start to fall over and die, it’s usually a sign that it’s time to harvest.
Harvesting Techniques
Be gentle during the harvest to avoid bruising the tubers. Use a spading fork to carefully lift the sweet potatoes out of the ground, being cautious to not stab them. Leave them in the sun for a few hours to dry before moving them into your storage area.
Conclusion: The Joy of Growing Sweet Potatoes
Growing sweet potatoes can be a rewarding experience that extends beyond the cultivation process. With careful planning, attention to detail, and a bit of patience, you can enjoy the fruits (or tubers!) of your labor in just a few months.





