In this post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about where to plant banana trees to ensure they thrive — from ideal climate conditions to soil types, sunlight exposure, and companion plants.
Understanding the Basics of Banana Trees

Before we dive into specifics, it’s essential to note that banana plants are not technically trees; they are large herbaceous plants. They belong to the genus Musa, and understanding their growth requirements is key to successful cultivation. Here’s what you need to know:
Climate Requirements: Bananas flourish in warm, tropical to subtropical climates. Most varieties prefer temperatures between 75°F and 95°F (24°C to 35°C) and should not be exposed to frost, as this can damage the plant.
Moisture Needs: Whether you’re planting in a humid environment or a dry one, banana plants require a lot of water. They thrive in moist but well-drained soil. Regular watering will be necessary, especially during dry spells.
Growth Patterns: Banana plants can grow quite tall, often reaching heights of 6 to 16 feet (2 to 5 meters), depending on the variety. This is crucial when considering where to plant them, as their height could overshadow smaller plants and affect your garden’s aesthetic or vegetable yield.
Ideal Planting Locations

When it comes to planting banana trees, the location inside your garden plays a significant role in their success. Let’s break this down into various essential aspects.
1. Sunlight Exposure
Banana trees thrive best in full sunlight. Ideally, they should receive anywhere from 12 to 14 hours of sunlight daily. Here are some considerations:
Direct Sunlight: Select a spot that receives full sun exposure throughout the day. While younger banana plants can tolerate some shade, mature plants require ample sunlight to produce fruit effectively.
Protection from Wind: While sun exposure is critical, it’s equally important to protect banana trees from strong winds. Wind can damage their large leaves and even knock over young plants. A location sheltered by a natural windbreak, such as a fence or larger plants, can help mitigate this.
2. Soil Quality and Drainage
The composition of your soil can heavily influence the health of your banana trees. Here’s what to consider:
Well-Drained Soil: Banana plants are susceptible to root rot, so well-draining soil is essential. Sandy loam soils with good drainage properties offer the best environment. Avoid heavy clay soils that retain water.
Soil pH: Aim for soil pH levels between 5.5 and 7.0 for optimal growth. Testing your soil can help you understand its current condition and inform decisions regarding amendments.
Nutrients: Enrich the soil with organic compost before planting. This not only improves drainage but provides nutrients essential for healthy growth. Incorporating aged manure or banana plant residues can also be beneficial.
Temperature Considerations
As mentioned earlier, banana trees are tropical plants. Therefore, the temperature in the area where you’re planting is crucial.
Cold Tolerance: Choose a planting spot that is less prone to frost. If you live in a marginal banana-growing area, consider planting next to south-facing walls or structures that retain heat, allowing for a warmer microclimate.
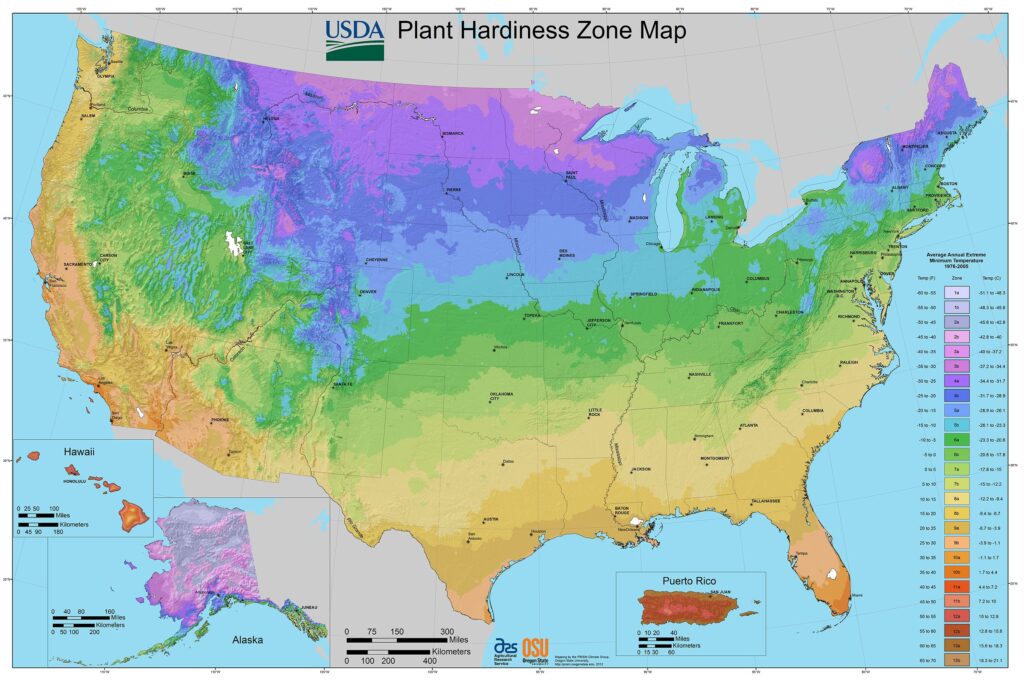
Climate Zones: Research your USDA hardiness zone. In the US, for instance, banana trees grow well in zones 9 through 11. If you live in a more temperate zone, you might need to employ container growing methods and bring your plants indoors during cold weather.
Spacing and Layout
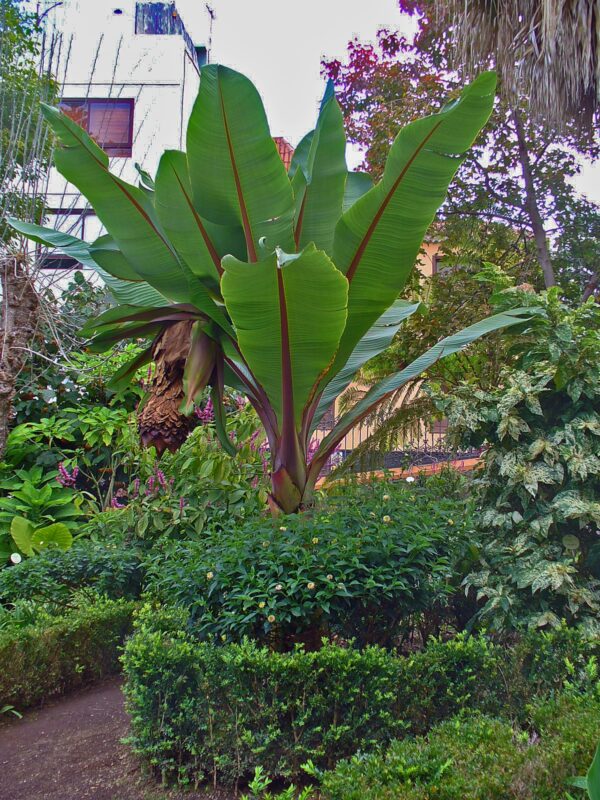

When planting bananas, spacing is another vital consideration to ensure your trees have enough room to grow and produce fruit.
Spacing Between Plants: Each banana plant needs space to spread its roots and leaves. A spacing of at least 8 to 10 feet (2.5 to 3 meters) between each plant is ideal. This prevents overcrowding, promotes good air circulation, and reduces the risk of disease.
Layout: Consider the layout of your garden. Arrange the banana trees in a way that allows easy access for maintenance and harvesting. Some gardeners choose to create a banana circle, which not only looks aesthetically pleasing but maximizes the use of the space.
Companion Planting

Companion plants can enhance the growth of banana trees and improve the health of your garden overall. Here’s how to integrate them effectively.
Planting with Pollinators: Flowers that attract bees and other pollinators can benefit banana trees. Integrating flowering plants like marigolds or sunflowers nearby can enhance fruit production through better pollination.
Nitrogen-Fixing Plants: Help enrich the soil around your bananas by planting nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes. These plants improve soil fertility, which is beneficial for the nutrient-hungry banana plants.
Pest Deterrents: Consider using companion plants that deter pests. For when banana plants are at risk from aphids or spider mites, planting herbs like basil or mint nearby can act as natural repellents.
Microclimates
Microclimates are small areas within your garden that have different environmental conditions than the surrounding areas. Identifying and utilizing microclimates can enhance your banana cultivation.
Tree Canopy: If you have an existing tree canopy that offers dappled sunlight, it can provide a perfect microclimate. Young banana plants can benefit from partial shade while still receiving enough light to grow.
Heat Reflecting Surfaces: Planting banana trees near concrete surfaces or patios can create a warmer microclimate due to heat reflection, which could be beneficial in cooler climates.
Container Planting
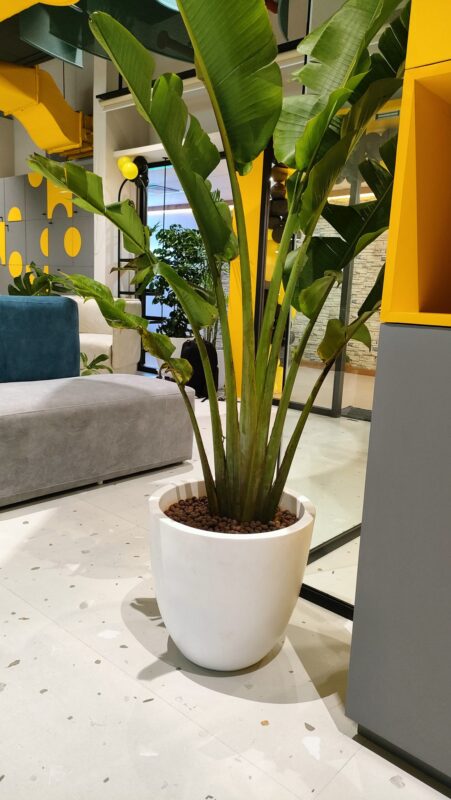

If space is limited or your climate isn’t ideal, consider planting bananas in containers. This method allows more control over their environment.
Choosing Containers: Make sure to select large containers (at least 15-20 gallons) with drainage holes. This enables root growth and prevents stagnation.
Mobility: One of the significant benefits of container planting is mobility. You can move your banana plants to sunny spots or sheltered locations as needed, adapting to changing weather conditions.
Seasonal Care
Finally, environmental conditions shift throughout seasons, and being aware of these changes will help you provide the best care for your banana trees.
Summer Care: During the growing season, ensure consistent moisture. Mulching around the base can help retain soil moisture and keep roots cool.
Winter Preparation: In cooler months, you will need to prepare your banana trees for a temperature drop. If planted in-ground, consider wrapping the base with insulating materials, and in containers, move them to a warmer area or indoors if necessary.
Conclusion
Planting banana trees can be a rewarding endeavor, yielding delicious fruit while adding a tropical vibe to your garden. Understanding where to plant these glorious plants is fundamental for their growth and productivity. By considering sunlight, soil quality, temperature, spacing, companion planting, microclimates, container options, and seasonal care, you will set the stage for healthy banana trees and ultimately enjoy the fruits of your labor.






