In this guide, we will dig into the optimal conditions, ideal locations, soil types, environmental considerations, and practical tips for successfully growing grapes.
Understanding the Grapevine

Before we explore the specifics of planting, it’s essential to understand why grapevines need particular conditions. Grapes belong to the genus Vitis, which is well adapted to a variety of climates but thrives in areas known for their warm summers and well-draining soils. By recognizing the fundamental growth requirements of grapevines, you will make informed decisions about where to plant them.
Climate Considerations
Grapevines flourish when they receive plenty of sunlight, warmth, and protection from harsh winds. Regions that offer a climate with warm temperatures during the day and cooler nights—particularly important for developing aromatic and flavorful grapes—are ideal. Depending on the grape variety, some vines may tolerate cooler temperatures, while others, like Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot, require a warmer climate.
Subsections:
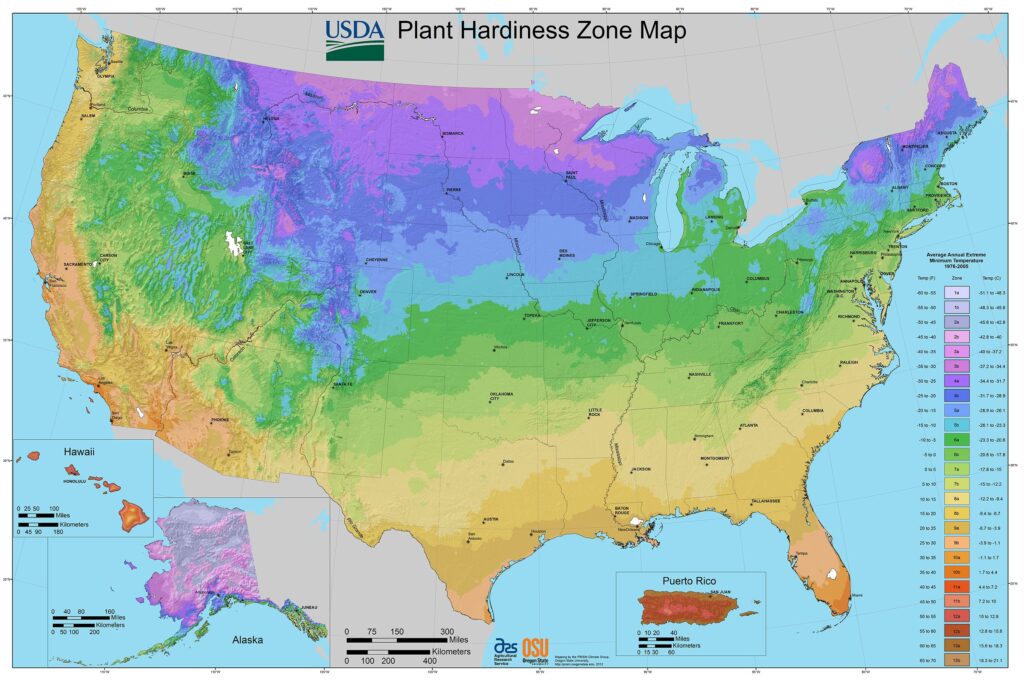
Hardiness Zones: Familiarize yourself with the USDA Hardiness Zones to determine the resilience of grape varieties in your area. Grapes typically grow well in zones 5 to 10, with much variance based on specific varietal needs.
Microclimates: Pay attention to local microclimates, which may differ from general region climates. Areas with stone walls, large bodies of water, or structures can create microclimates that provide protection and warmth.
Frost Risks: Late spring and early fall frosts can damage young shoots and buds, so consider planting grapes in areas that are less prone to frost.
Selecting the Right Location

Finding the perfect location for your grapevines involves evaluating several factors. Grapes require specific exposures, elevations, and other site characteristics to thrive.
Sunlight Exposure
One of the most critical factors for grape cultivation is sunlight. Ideally, grapevines require at least 6 to 8 hours of full sun each day.
Southern Exposure: Planting your grapevines in south-facing areas maximizes sun exposure. This positioning ensures that vines receive the necessary light, especially in the morning when sunlight is less intense.
Avoiding Shade: Evaluate nearby vegetation or structures that may cast shadows on your vines. Even partial shade can hinder grape development, leading to lower yields.
Soil Quality and Drainage
The soil type and its drainage capacity directly influence the health of your grapevines.
Ideal Soil Types: Grapes prefer sandy loam or loamy soil rich in organic matter. These types provide essential nutrients and allow for good root development.
Soil Testing: Conducting a soil test is an excellent first step. This analysis will help you understand the pH level and nutrient content, guiding any necessary amendments.
Drainage Solutions: Grapes are sensitive to waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. If your soil has poor drainage, consider mounding, utilizing raised beds, or amending with organic matter to improve drainage capacity.
Topography and Elevation
The physical layout of your land can substantially impact grape growth.
Slope of Land: Slightly sloped areas are advantageous as they promote drainage and reduce the risk of frost accumulation. A slope can also enable better air circulation around the vines.
Elevation: Higher elevations often have cooler temperatures and might experience different sunlight patterns. Selecting an elevation with ample sunlight exposure helps balance temperature fluctuations.
Grapevine Varietal Considerations
When determining where to plant grapes, the specific varietal you choose will influence your site selection. Different grape varieties have unique requirements and preferences regarding sunlight, climate, and soil composition.
Popular Grape Varieties
Cabernet Sauvignon: This variety thrives in warm climates, preferring well-drained soils and full sun exposure. Ideal regions include California’s Napa Valley and Bordeaux in France.
Chardonnay: Versatile and adaptable, Chardonnay can be grown in various soils, yet it benefits from sunny slopes. Cooler regions produce grapes with more acidity.
Zinfandel: Best suited for warm, dry climates, this variety flourishes in sandy loam soils. California’s climate proves ideal for Zinfandel cultivation.
Concord: Known for its robust flavor, this variety grows well in a range of climates but prefers the temperate conditions often found in New York and northern states.
Matching Varietals to Location
Choosing a grape variety aligned with your locale’s climate and soil will enhance your chances of a successful harvest. Investigate local viticulture practices or seek advice from nearby vineyards that share similar conditions.
Soil Preparation for Grapes

Once you’ve decided where to plant your grapes, preparing the soil is a crucial next step. Proper soil preparation ensures that your vines will establish themselves quickly and healthily.
Testing and Amending Soil
Conducting a soil test will reveal pH levels and nutrient content. Grapes prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH (between 6.0 and 7.0).
Adding Nutrients: Depending on soil test results, you may need to add organic matter or fertilizers to support healthy vine growth. Well-rotted compost or aged manure can improve nutrient levels and soil structure.
Correcting pH Levels: If your soil is too acidic or too alkaline, amendments like lime (to raise pH) or sulfur (to lower pH) will help you reach the ideal level.
Tilling and Rusticity
Tilling the Soil: Tilling helps to aerate the soil, allowing roots to penetrate more deeply. This process also incorporates any amendments more effectively.
Sustainable Practices: Consider utilizing cover crops in between vine rows to enhance soil quality and prevent erosion. Leguminous cover crops can add nitrogen back into the soil.
Planting Techniques for Success

With your site and soil prepared, it’s time to plant your grapevines. The technique used during planting can have lasting effects on their development and future health.
Timing the Planting
The best time to plant grapevines is during the spring when the soil temperature has warmed sufficiently. This timing ensures that your vines take root before the summer heat sets in.
Spacing and Layout
Proper spacing allows enough air circulation between plants, reducing the risk of disease.
Row Orientation: Rows should be planted east to west to capture maximum sunlight. This orientation promotes uniform growth and helps with wind protection.
Spacing Between Vines: Generally, vines should be spaced 6 to 10 feet apart, depending on the variety and intended training system.
Techniques for Planting
Digging Holes: Create holes deep enough to accommodate the root ball of new vines while still allowing the graft union to sit above the ground.
Backfilling and Watering: After placing the vine in the hole, backfill with soil and water thoroughly to eliminate air pockets.
Training and Trellising
As grapevines grow, they require proper training and support to ensure healthy development and yield.
Selecting a Trellis System
The choice of a trellis system depends on your vineyard size and the grape varietals you are growing.
Vertical Shoot Positioning (VSP): This method encourages vertical growth, allowing for even sunlight exposure and easy harvesting. Ideal for many wine grape varieties.
Geneva Double Curtain: This system is beneficial for high-yielding varieties, enabling greater productivity per acre.
Single Wires and Arbors: For home gardens, simpler systems might suffice. Creating a simple arbor can enhance aesthetic appeal while still supporting vine growth.
Training Techniques
Pruning: Regular pruning is essential to control vine growth, maintain fruit quality, and prevent disease. Prune in the winter when vines are dormant to guide growth.
Canopy Management: Managing foliage is vital for proper sunlight exposure, air circulation, and maintaining appropriate moisture levels.
Caring for Your Grapes
Once planted, ongoing care is essential for the health of your grapevines.
Watering Practices
Grapevines establish a deep root system that can tap into groundwater, reducing the need for frequent watering. However, consistent moisture is critical during the first few weeks after planting.
Drip Irrigation: Consider using drip irrigation for precise watering, as it minimizes water waste while meeting the vines’ needs.
Fertilization
Regular fertilization throughout the growing season ensures that your vines receive the necessary nutrients.
Organic Options: Organic fertilizers such as compost tea or fish emulsion can enhance soil health and promote strong vine growth.
Pest and Disease Management
Being proactive about pest and disease control will save you significant trouble down the road.
Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect your vines for signs of pests, such as aphids or spider mites, and be vigilant for potential diseases like powdery mildew. Early detection is key to effective management.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Consider utilizing IPM strategies, which focus on ecological balance and target specific pests without harming beneficial insects.
Harvesting Your Grapes
After considerable care and attention to your grapevines, the time to harvest arrives.
Timing the Harvest
Understanding when your grapes are ripe is crucial. Grapes reach maturity at different times, typically late summer to early fall, depending on your location and varietals.
Taste Testing: Regularly taste the grapes as they approach maturity. The sweetness, acidity, and overall flavor are excellent indicators of readiness.
Sugar Levels: Use a refractometer to measure the sugar levels if you’re growing wine grapes, as this will help determine optimal harvest time.
Harvest Techniques
Gentle Handling: Handle grape clusters gently to avoid bruising, especially if they are meant for winemaking.
Using Clean Tools: Equip yourself with clean clippers or scissors to minimize infection risks during the harvest process.









