In this guide, we’ll explore the ideal conditions, considerations, and locations for planting raspberries to ensure a bountiful harvest.
Understanding Raspberry Varieties

Before choosing a planting site, it’s important to know that not all raspberries are created equal. There are two main types of raspberries: summer-bearing and everbearing (also known as fall-bearing).
Summer-bearing raspberries produce fruit on second-year canes during the summer months, while everbearing varieties can produce fruit in the summer and again in the fall, with some varieties also yielding on first-year canes. Understanding the specific needs of the variety you choose can help determine the best location for planting.
Ideal Climate Conditions
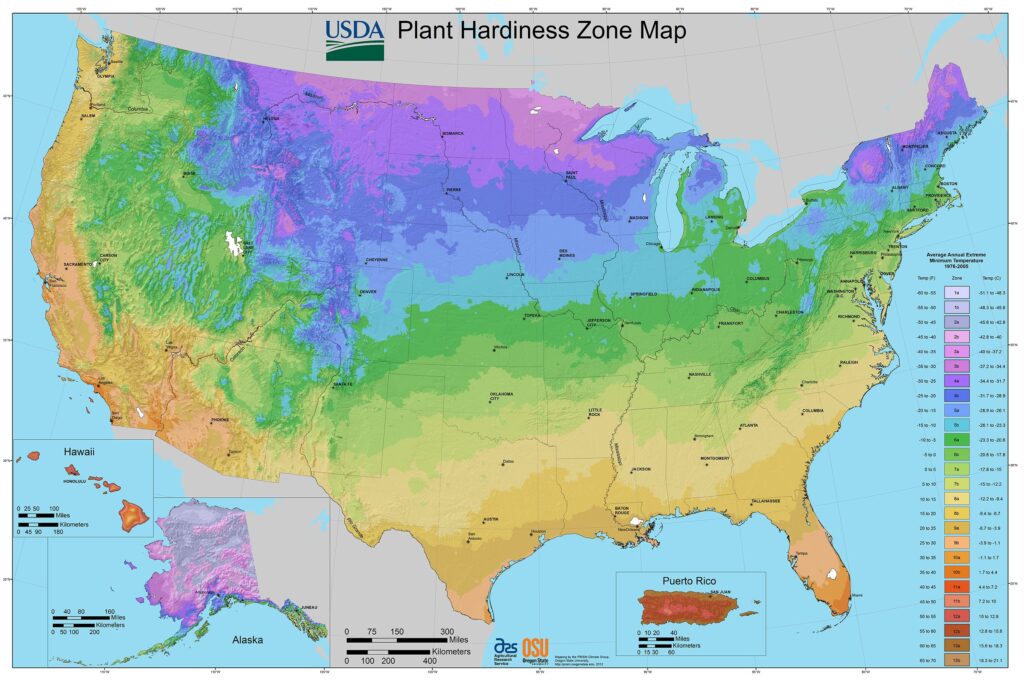
Raspberries thrive in temperate climates. They prefer regions where summers are warm, but not scorching, and winters are cold enough to require a dormancy period. Here are a few climate considerations:
Temperature Range
Raspberry plants generally flourish in temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C) during the growing season. While established plants can tolerate cooler temperatures, an ideal area can promote stronger growth and fruit production. Zones 3 to 8 on the USDA hardiness scale are typically suitable for growing raspberries, but local climate conditions should also be factored in.
Frost Considerations
Location is vital in relation to frost. Late spring frosts can damage delicate blossoms, so it’s essential to choose a site that tends to warm up early in the season or where frost is less likely. Areas with good air drainage, such as being slightly elevated, can prevent frost pockets that could jeopardize your raspberry plants.
Sunlight: The Key to Bountiful Berries

Raspberries are sun-loving plants that require full sunlight for optimal growth. Ideally, they should receive at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Here are some considerations when determining the best sun exposure:
Sun Orientation
When selecting an area in your garden for raspberries, consider east or south-facing locations that get ample sunlight throughout the day. Avoid planting in shaded areas, such as alongside taller trees or structures that may block sunlight as they grow.
Impact of Shadows
Monitor your garden throughout the day to ensure that the raspberry location won’t occasionally fall into shadow, especially in the late afternoon, which can reduce the sunlight they receive. This exposure is crucial not only for fruiting but also for the overall health of the plants.
Soil Quality: Preparing the Perfect Bed

Raspberries prefer well-draining, sandy loam soils rich in organic matter. The pH level should ideally be between 5.5 and 6.5. Here’s how to assess and prepare the soil for raspberry planting:
Testing Soil Health
Before planting, it’s wise to conduct a soil test. This will inform you about nutrient levels and pH. Many local agricultural extensions provide testing services, and based on the results, you can amend your soil as needed to create an ideal growing environment.
Soil Amendments
To improve soil quality, consider incorporating well-rotted manure, compost, or peat moss into the planting site. These amendments will increase nutrient content and enhance soil structure for better moisture retention and drainage, both critical for raspberry growth.
Space and Planting Layout

Raspberries can spread quite a bit, so adequate spacing is crucial for healthy plants and ease of maintenance. Here are some guidelines:
Recommended Spacing
When planting raspberries, they should generally be spaced 2 to 3 feet apart. If you are planting rows, aim for 6 to 8 feet between rows to allow ventilation and easy access for harvesting and maintenance.
Trellising Considerations
Raspberry canes benefit from a trellising system, which can support their upright growth and improve air circulation. Depending on the variety, you can use a simple two-wire trellis or a more robust system with posts. This setup allows you to keep the plants off the ground, reducing disease risk and facilitating easier harvesting.
Drainage Matters: Avoiding Waterlogged Roots

One of the biggest challenges in raspberry cultivation is ensuring proper drainage. Raspberry roots are sensitive to waterlogged soil, which can lead to root rot and other diseases. Here’s how to tackle drainage:
Assessing Drainage
If you’re uncertain about the drainage quality in your chosen spot, perform a simple test. Dig a hole about 12 inches deep and fill it with water. If the water hasn’t drained within a few hours, you may need to consider alternative planting sites or create raised beds to improve drainage.
Raised Beds
In areas where drainage is poor, creating raised beds can significantly enhance the growing conditions for raspberries. Constructing a raised bed allows excess water to drain away from the roots more effectively and creates an ideal microclimate for raspberries.
Water Supply: Ensuring Consistent Irrigation
Raspberry plants require consistent moisture, especially during their fruiting stage. Here’s how to ensure they have the right amount of water:
Irrigation Systems
Whether you opt for drip irrigation, soaker hoses, or overhead watering, aim for a system that allows water to penetrate the soil deeply. Raspberries thrive when their roots receive consistent moisture without sitting in water.
Mulching
Applying a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plants can significantly help retain soil moisture while suppressing weeds. Consider using straw, wood chips, or grass clippings as mulch material, ensuring you keep it a few inches away from the plant stem to prevent rot.
Companion Planting: Choosing Neighbors Wisely

Companion planting involves strategically placing different plants near each other to improve growth, deter pests, and enhance the overall health of the garden. Some beneficial companions for raspberries include:
Good Neighbors
Herbs like basil, chives, and mint can repel certain pests while attracting beneficial insects. Additionally, planting garlic or onions nearby can deter aphids and other harmful pests that might target your raspberries.
Poor Companions
Be cautious about planting raspberries near nightshades, such as tomatoes and peppers, as these plants are susceptible to similar diseases that can affect raspberries as well. Evidence suggests that they may also compete for nutrients in the soil.
Maintenance as You Grow

Planting your raspberries is just the beginning; ongoing maintenance is critical to ensure healthy plants and a productive harvest.
Pruning Practices
Regular pruning is essential for maintaining raspberry health and maximizing yields. For summer-bearing raspberries, prune away the canes that bore fruit after harvest, as these will not produce again. Always leave new canes to grow, which will bear fruit the following year. For everbearing raspberries, you can actually prune all canes to the ground after harvest for optimal fall yields or leave some for summer production.
Pest and Disease Management
Be vigilant about monitoring your raspberry plants for signs of pests or diseases. Common issues include spider mites, aphids, and diseases like powdery mildew and root rot. Implement organic control methods, such as insecticidal soap or neem oil, and ensure good air circulation to minimize these risks.
Seasonal Considerations: Timing Your Planting
The time at which you plant can have a major impact on the success of your raspberry patch.
Spring Planting
Late winter or early spring is often the best time to plant raspberries, just as the soil begins to warm. This allows the plants to establish roots throughout the growing season in optimal conditions.
Fall Planting
If you live in a warm climate, fall planting can also work, provided there’s enough time for the roots to establish before the first hard freeze. However, be mindful that plants will need adequate mulch and protection to survive the winter months.
Conclusion: Planting for Success
Choosing the right planting site for raspberries is crucial for maximizing their potential and ensuring a healthy yield. From considering climate conditions and sunlight to understanding soil needs and maintaining proper care, each factor plays a vital role in the success of your raspberry plants.






